Art Labeling Activity Sound and Hearing Reception and Transduction of Sound Enerygy
three.ii The anatomy of the cochlea
The cochlea has a spiral shape resembling the beat out of a snail (Figure 4a). You tin can approximate the structure of the cochlea by wrapping a drinking straw 2.five times around the tip of a sharpened pencil. The hollow tube, represented by the harbinger, has walls fabricated of bone and the fundamental pillar of the cochlea, represented by the pencil, is a conical bony structure called the modiolus. Unravelled (Figure 4b), the cochlea's hollow tube is about 32 mm long and 2 mm in diameter. The tube of the cochlea is divided into three chambers: the scala vestibuli, the scala media (or cochlear duct) and the scala tympani. The three scalae wrap around inside the cochlea similar a spiral staircase ('scala' is Latin for 'stairway'). The scala vestibuli forms the upper bedroom and at the base of operations of this bedroom is the oval window. The lowermost of the iii chambers is the scala tympani. It too has a basal aperture, the circular window, which is closed by an elastic membrane. The scala media or cochlear duct separates the other 2 chambers along most of their length. The first of the cochlea, where the oval and circular windows are located is known as the basal end, while the other terminate, the inner tip is known as the apical stop (or apex). The scala vestibuli and the scala tympani communicate with 1 another via the helicotrema, an opening in the cochlear duct at the apex. Both scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with the aforementioned fluid, known as perilymph (essentially the same in composition as the extracellular fluid bathing about of the nervous system), while the scala media is filled with endolymph (with very high potassium and low sodium concentrations).
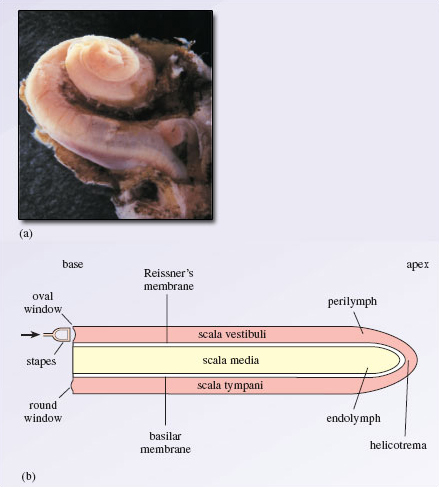
Figure 4(a): Picture by Mireille Lavigne-Rabillard, from 'Promenade around the cochlea', by R. Pujol, S. Blatrix, T.Pujol and V. Reclar-Enjalbert, CRIC, University Montpelli ©
Figure 4 (a): Pic past Mireille Lavigne-Rabillard, from 'Promenade effectually the cochlea', by R. Pujol, S. Blatrix, T.Pujol and Five. Reclar-Enjalbert, CRIC, Academy Montpelli
Figure 4 (a) coiled cochlea of a human foetus of five months gestation (magnification × 40); (b) diagrammatic representation of the iii scalae of the cochlea (uncoiled)
Effigy v is a cross-department of the cochlea showing the three chambers which run forth its length. Between the scala vestibuli and the scala media is a membrane called Reissner's membrane and betwixt the scala tympani and the scala media is the basilar membrane. Lying on top of the basilar membrane within the cochlear duct is the organ of Corti and hanging over the organ of Corti, is the tectorial membrane. The collective term for the partitions of the scala media (the organ of Corti, the basilar membrane and the tectorial membrane) is the cochlear sectionalisation.
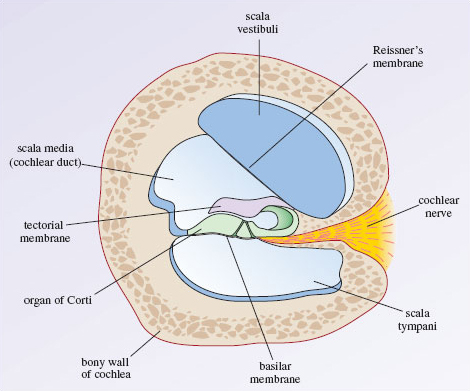
Figure 5 Cantankerous-section of the cochlea
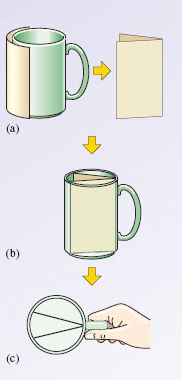
Figure vi Construction of a 'cochlea'
The post-obit uncomplicated activity will help you understand the structure of the cochlea more than clearly. Imagine that your empty java mug (assuming it's a cylindrical shape, or thereabouts) represents a section of the uncoiled tube-like cochlea. Take a piece of paper that is about the same summit equally the mug and that is broad enough to wrap halfway around the mug (Figure 6a). Fold it in half and insert it into the centre of the mug then that the fold runs vertically downwardly the side of the mug where the handle is located (Figure 6b). The paper should lie across the middle of the mug. Now (if necessary) split the two pieces of newspaper then that they form a 5-shape (Effigy 6c). Yous now have the basic construction of the cochlea. If you hold the mug by the handle in your right hand and look straight into it, you lot accept the same view as that shown in Figure v. Compare Figure 5 to your 'cochlea' and answer the following questions:
Activeness
What construction does the pinnacle piece of paper represent?
Answer
Reissner'due south membrane.
Activity
What does the space to a higher place the height slice of paper correspond?
Answer
The scala vestibuli.
Activity
What does the bottom slice of paper represent?
Answer
The basilar membrane.
Action
What does the space below the bottom piece of paper represent?
Action
What does the 5-shaped infinite stand for?
Answer
The scala media (or cochlear duct).
The scala media houses the organ of Corti. The organ of Corti and all its associated structures (including the hair cells, see below) runs the length of the basilar membrane (from the top to the bottom of your mug) as does the overlying tectorial membrane.
An enlargement of the organ of Corti is shown in Effigy seven. The organ of Corti is the primary auditory receptor structure and houses the sensory receptor cells which are known as pilus cells because each has about 100 hair-like stereocilia extending from its apical end which are embedded in the tectorial membrane. You can encounter that the pilus cells are of 2 types: outer hair cells and inner hair cells, which are separated past a rigid inverted V-shaped structure known as Corti's arch.
We shall return to the organ of Corti and the hair cells and their involvement in the transduction of an auditory signal into neural data in Department iii.4. For now, nosotros need to consider the basilar membrane and in particular, its response to vibrations in the cochlear fluid.

Effigy 7(b): Copyright © Science Photo Library ©
Figure seven(b): Copyright © Science Photo Library
Figure seven: The organ of Corti: (a) sketch cross-department. (b) Coloured scanning electron micrograph. Four rows of hair cells can be seen, which are supported by colonnade cells (magnification ×600).
Source: https://www.open.edu/openlearn/science-maths-technology/biology/hearing/content-section-3.2
0 Response to "Art Labeling Activity Sound and Hearing Reception and Transduction of Sound Enerygy"
Publicar un comentario